Jaundice
Jaundice is a medical condition in which there is an abnormal accumulation of bilirubin in the body, leading to yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes. Bilirubin is a waste product produced when the liver breaks down red blood cells. It is normally processed and eliminated by the liver, but when there is a problem with the liver’s ability to process bilirubin, it can build up in the body and cause jaundice.
Jaundice disease should be treated in prior time so get consult yourself at Mediliv Hospital by best jaundice doctor in Nashik. Dr. Deepika Mundada is the jaundice specialist in Nashik.
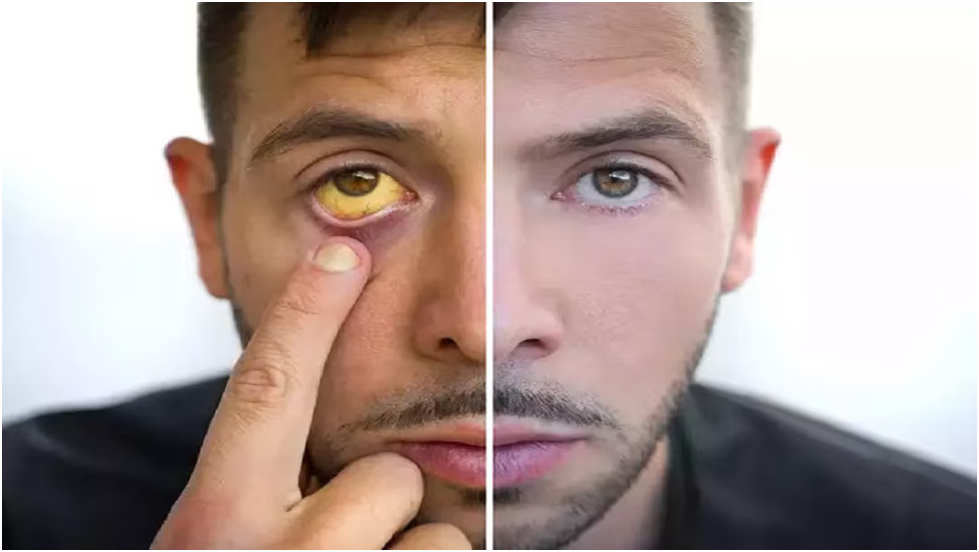
Jaundice can have a variety of causes, including liver diseases such as hepatitis or cirrhosis, blockage of the bile ducts, hemolytic anemia, and certain medications or toxins. In infants, jaundice is common and is often caused by an immature liver that is not yet fully able to process bilirubin.
Treatment for jaundice depends on the underlying cause. In some cases, treatment may not be necessary and the condition will resolve on its own. In other cases, treatment may involve medications to help the liver process bilirubin, procedures to remove blockages in the bile ducts, or even liver transplant in severe cases If you have symptoms of jaundice, it’s crucial to contact a doctor right once because they could indicate a more serious underlying problem.
Causes of jaundice
Jaundice can have a variety of causes, including:
Liver diseases: Hepatitis (inflammation of the liver), alcoholic liver disease, cirrhosis (scarring of the liver tissue), and liver cancer can all cause jaundice.
Bile duct obstruction: When the bile ducts that carry bile from the liver to the small intestine are blocked, bile can back up in the liver and cause jaundice. This can be caused by gallstones, tumors, or strictures (narrowing) of the bile ducts.
Hemolytic anemia: When red blood cells are broken down too quickly, more bilirubin is produced than the liver can process, leading to jaundice. This can be caused by inherited conditions such as sickle cell anemia or thalassemia, or by certain medications or infections.
Newborn jaundice: Infants are often born with jaundice due to an immature liver that is not yet fully able to process bilirubin. This typically gets better on its own in a few weeks.
Gilbert’s syndrome: This is a genetic condition in which the liver is unable to process bilirubin effectively, leading to mild jaundice.
Dubin-Johnson syndrome and Rotor syndrome: These are rare genetic conditions that can cause mild to moderate jaundice.
Certain medications or toxins: Some medications, such as acetaminophen, can cause liver damage and jaundice if taken in large doses. Exposure to certain toxins, such as industrial chemicals or mushrooms, can also cause jaundice.
It’s important to see a doctor if you are experiencing symptoms of jaundice, as it can be a sign of a serious underlying condition.
Symptoms of jaundice
Jaundice’s most common symptom is a yellowing of the skin and eye whites. However, there are other symptoms that may accompany jaundice, including:
- Whites of the eyes and skin become yellow
- Dark urine
- Pale stools
- Fatigue
- Abdominal pain or swelling
- Itching
- Nausea and vomiting
- Loss of appetite
- Unintentional weight loss
- Fever
- Joint pain
It’s important to note that not everyone with jaundice will experience all of these symptoms, and some people with jaundice may not experience any symptoms at all. In addition, some of these symptoms may be indicative of other medical conditions, so it’s important to see a doctor for a proper diagnosis. If you notice any yellowing of your skin or eyes, it’s important to seek medical attention promptly, as jaundice can be a sign of a serious underlying condition.
Treatment of jaundice
The underlying cause determines how to treat jaundice.. In some cases, jaundice may resolve on its own without any specific treatment. In other cases, treatment may be necessary to manage the underlying condition and relieve symptoms.
Some common treatments for jaundice include:
Treating the underlying condition: Depending on the cause of jaundice, treatment may involve medications, surgery, or other interventions to address the underlying condition.
Managing symptoms: If you are experiencing symptoms such as itching or fatigue, your doctor may prescribe medications to help manage these symptoms.
Lifestyle changes: If your jaundice is caused by alcohol or drug use, your doctor may recommend that you make lifestyle changes to reduce or eliminate your consumption of these substances.
Phototherapy: In newborns with jaundice, phototherapy (exposure to special lights) may be used to help break down bilirubin and reduce symptoms.
Liver transplant: In rare cases where jaundice is caused by severe liver damage, a liver transplant may be necessary.
It’s important to see a doctor if you are experiencing symptoms of jaundice, as it can be a sign of a serious underlying condition. Your doctor can perform tests to determine the cause of your jaundice and recommend an appropriate course of treatment.
Risk factors of jaundice
There are several risk factors that can increase the likelihood of developing jaundice. Some of these risk factors include:
Liver disease: People with liver disease, such as hepatitis or cirrhosis, are at an increased risk of developing jaundice.
Bile duct obstruction: Obstruction of the bile ducts, which carry bile from the liver to the small intestine, can cause jaundice. This can be caused by gallstones, tumors, or strictures (narrowing) of the bile ducts.
Hemolytic anemia: Hemolytic anemia is a condition in which red blood cells are broken down too quickly, leading to an excess of bilirubin in the body and an increased risk of jaundice. This can be caused by inherited conditions such as sickle cell anemia or thalassemia, or by certain medications or infections.
Newborns: Newborns are at a higher risk of developing jaundice due to an immature liver that is not yet fully able to process bilirubin.
Age: Older adults are at an increased risk of developing jaundice due to age-related changes in liver function.
Alcohol and drug use: Heavy alcohol and drug use can cause liver damage and increase the risk of developing jaundice.
Infections: Infections such as hepatitis A, B, and C can damage the liver and increase the risk of jaundice.
It’s important to note that having one or more of these risk factors does not necessarily mean that you will develop jaundice. However, if you have any of these risk factors, it’s important to discuss your risk of developing jaundice with your doctor and take steps to reduce your risk.
Prevention of jaundice
Prevention of jaundice involves addressing the underlying causes that can lead to the condition. Here are some general measures that can help reduce the risk of developing jaundice:
Maintain a healthy diet: Eating a well-balanced diet that includes plenty of fruits and vegetables can help promote liver health and reduce the risk of liver disease.
Avoid alcohol and drugs: Excessive alcohol consumption and drug use can damage the liver and increase the risk of developing jaundice.
Practice safe sex: Hepatitis B and C are sexually transmitted infections that can lead to liver damage and jaundice. Practicing safe sex can help reduce the risk of contracting these infections.
Get vaccinated: Vaccinations are available for hepatitis A and B, which can help reduce the risk of developing these infections and subsequent liver damage.
Practice good hygiene: Practicing good hygiene, such as washing your hands regularly, can help reduce the risk of contracting infections that can cause liver damage and jaundice.
Manage chronic medical conditions: If you have a chronic medical condition such as diabetes or high blood pressure, it’s important to manage the condition to reduce the risk of developing liver disease.
Get regular check-ups: Regular check-ups with your doctor can help detect liver disease early, before it progresses to the point of causing jaundice.
While not all cases of jaundice can be prevented, taking these steps can help reduce the risk of developing the condition and promote overall liver health.
