Gastrointestinal System
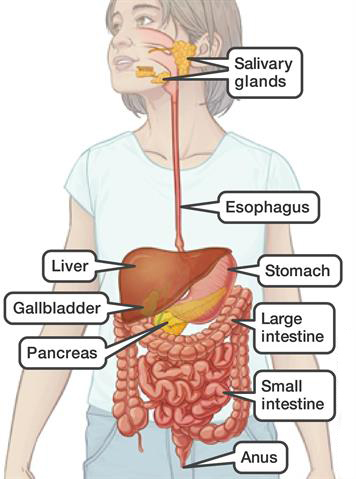
The gastrointestinal tract (GIT) consists of a hollow muscular tube starting from the oral cavity, where food enters the mouth, continuing through the pharynx, oesophagus, stomach and intestines to the rectum and anus, where food is expelled. There are various accessory organs that assist the tract by secreting enzymes to help break down food into its component nutrients. Thus the salivary glands, liver, pancreas and gall bladder have important functions in the digestive system. Food is propelled along the length of the GIT by peristaltic movements of the muscular walls.
The primary purpose of the gastrointestinal tract is to break food down into nutrients, which can be absorbed into the body to provide energy. First food must be ingested into the mouth to be mechanically processed and moistened. Secondly, digestion occurs mainly in the stomach and small intestine where proteins, fats and carbohydrates are chemically broken down into their basic building blocks. Smaller molecules are then absorbed across the epithelium of the small intestine and subsequently enter the circulation. The large intestine plays a key role in reabsorbing excess water. Finally, undigested material and secreted waste products are excreted from the body via defecation (passing of faeces).
How does food move through my GI tract?
Food moves through your GI tract by a process called peristalsis. The large, hollow organs of your GI tract contain a layer of muscle that enables their walls to move. The movement pushes food and liquid through your GI tract and mixes the contents within each organ. The muscle behind the food contracts and squeezes the food forward, while the muscle in front of the food relaxes to allow the food to move.
- Mouth. Food starts to move through your GI tract when you eat. When you swallow, your tongue pushes the food into your throat. A small flap of tissue, called the epiglottis, folds over your windpipe to prevent choking and the food passes into your esophagus.
- Esophagus. Once you begin swallowing, the process becomes automatic. Your brain signals the muscles of the esophagus and peristalsis begins.
- Lower esophageal sphincter. When food reaches the end of your esophagus, a ringlike muscle—called the lower esophageal sphincter —relaxes and lets food pass into your stomach. This sphincter usually stays closed to keep what’s in your stomach from flowing back into your esophagus.
- Stomach. After food enters your stomach, the stomach muscles mix the food and liquid with digestive juices. The stomach slowly empties its contents, called chyme, into your small intestine.
- Small intestine. The muscles of the small intestine mix food with digestive juices from the pancreas, liver, and intestine, and push the mixture forward for further digestion. The walls of the small intestine absorb water and the digested nutrients into your bloodstream. As peristalsis continues, the waste products of the digestive process move into the large intestine.
- Large intestine. Waste products from the digestive process include undigested parts of food, fluid, and older cells from the lining of your GI tract. The large intestine absorbs water and changes the waste from liquid into stool. Peristalsis helps move the stool into your rectum.
- Rectum. The lower end of your large intestine, the rectum, stores stool until it pushes stool out of your anus during a bowel movement.
